
* 645 OCEAN ROAD * POINT PLEASANT, NEW JERSEY 08742 * PHONE 800-714-1907 * FAX 732-714-1913 *
Table of Contents
1. General Information
2. Case History
3. Job Information
This data is usually obtained from the referring case manager or directly
from the Examinee's employer. If no job description is available a description is
obtained from the Dictionary of Occupational Titles (DOT).
4. Neck Kinematics
A computer kinematic assessment is performed for cervical flexion/extension,
lateral flexion and rotation. The Examinee is asked to perform each maneuver 8-10 repetitions
to full range and as quickly as possible. The events are video taped in a precisely
calibrated field for computer analysis. Each event is analyzed for total dynamic
range of motion and peak velocity quantity and quality. Consistency of results
is considered for determining Examinee effort.
After a thorough discussion of expectations, and agreement of understanding by the Examinee,
the Examinee is asked to perform the movement events.
Cervical Flexion/Extension
|
Chart 1:
Cervical Flexion/Extension
|
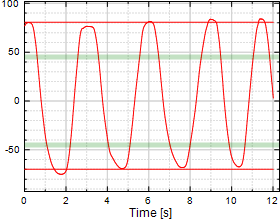
|
|
|
Table 1:
Cervical Flexion/Extension
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
Cervical Lateral Flexion
|
Chart 2:
Cervical Lateral Flexion
|
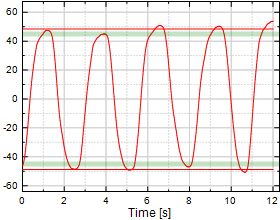
|
|
|
Table 2:
Cervical Lateral Flexion
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
Cervical Rotation
|
Chart 3:
Cervical Rotation
|
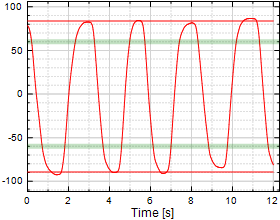
|
|
|
Table 3:
Cervical Rotation
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
Summary 4:
Neck Kinematics
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
0
of
6
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
1
of
6
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
0
of
0
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
0
of
0
Significant Findings Neck Kinematics:
5. Shoulder Kinematics
A computer kinematic assessment is performed for shoulder flexion/extension,
abduction/adduction, internal and external rotation. The Examinee is asked to
perform each maneuver 8-10 repetitions to full range and as quickly as possible.
The events were video taped in a precisely calibrated field for computer analysis.
Each event is analyzed for total dynamic range of motion and peak velocity quantity
and quality. Consistency of results is considered for
determining Examinee effort. After a thorough discussion of expectations, and
agreement of understanding by the Examinee, the Examinee is asked to perform
the movement events.
Shoulder Flexion/Extension
|
Chart 4:
Shoulder Flexion/Extension
|
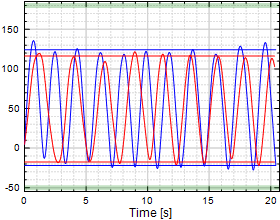
|
|
|
Table 4:
Shoulder Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
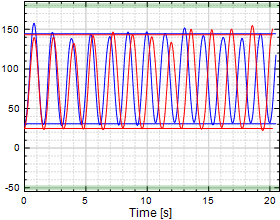
Shoulder Abduction/Adduction
|
Chart 5:
Shoulder Abduction/Adduction
|
|
|
|
Table 5:
Shoulder Abduction/Adduction
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
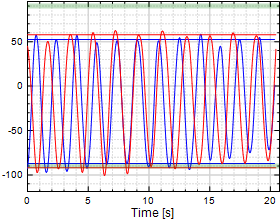
Shoulder Internal/External Rotation
|
Chart 6:
Shoulder Internal/External Rotation
|
|
|
|
Table 6:
Shoulder Internal/External Rotation (I/R)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
Summary 5:
Shoulder Kinematics
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
10
of
12
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
3
of
12
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
2
of
6
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
1
of
6
Significant Findings Shoulder Kinematics:
6. Elbow Kinematics
A computer kinematic assessment is performed for elbow flexion/extension,
and forearm supination/pronation. The Examinee is asked to perform each maneuver
8-10 repetitions to full range and as quickly as possible. The events are video taped
in a precisely calibrated field for computer analysis. Each event is analyzed for
total dynamic range of motion and peak velocity quantity and quality.
Consistency of results is considered for determining
Examinee effort. After a thorough discussion of expectations, and agreement of
understanding by the Examinee, the Examinee is asked to perform the
movement events.
|
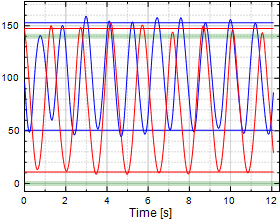
Chart 7:
Elbow Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 7:
Elbow Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
Summary 6:
Elbow Kinematics
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
2
of
4
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
2
of
4
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
1
of
2
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
1
of
2
Significant Findings Elbow Kinematics:
7. Wrist Kinematics
A computer kinematic assessment is performed for wrist flexion/extension,
ulnar/radial deviation and supination/pronation. The Examinee is asked to
perform each maneuver 8-10 repetitions to full range and as quickly as possible.
The events are video taped in a precisely calibrated field for computer analysis.
Each event is analyzed for total dynamic range of motion and peak velocity quantity
and quality. Consistency of results is considered for
determining Examinee effort. After a thorough discussion of expectations, and
agreement of understanding by the Examinee, the Examinee is asked to perform
the movement events.
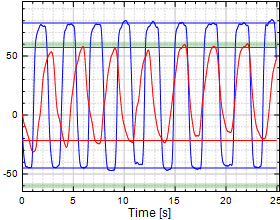
Wrist Flexion/Extension
|
Chart 8:
Wrist Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 8:
Wrist Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
Wrist Ulnar/Radial Deviation
|
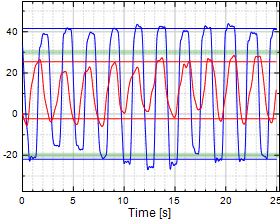
Chart 9:
Wrist Ulnar/Radial Deviation
|
|
|
|
Table 9:
Wrist Ulnar/Radial Deviation (U/R)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
Forearm Supination/Pronation
|
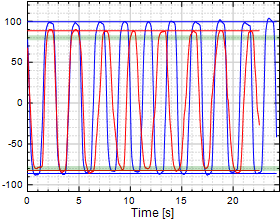
Chart 10:
Forearm Supination/Pronation
|
|
|
|
Table 10:
Forearm Supination/Pronation (S/P)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
Summary 7:
Wrist Kinematics
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
4
of
12
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
6
of
12
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
0
of
6
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
6
of
6
Significant Findings Wrist Kinematics:
8. Finger Kinematics
A computer kinematic assessment is performed for index finger flexion/extension.
The Examinee is asked to perform each maneuver 8-10 repetitions to full range and as quickly as possible.
The events are video taped in a precisely calibrated field for computer analysis.
Each event is analyzed for total dynamic range of motion and peak velocity quantity
and quality. Consistency of results is considered for
determining Examinee effort. After a thorough discussion of expectations, and
agreement of understanding by the Examinee, the Examinee is asked to perform
the movement events.
|
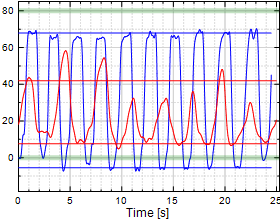
Chart 11:
Finger MP Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 11:
Finger MP Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
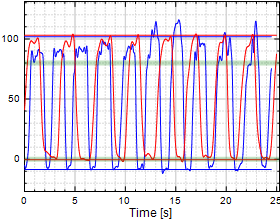
Chart 12:
Finger PIP Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 12:
Finger PIP Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
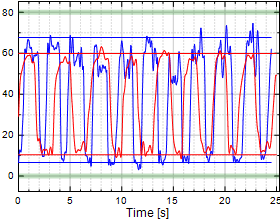
Chart 13:
Finger DIP Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 13:
Finger DIP Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
Summary 8:
Finger Kinematics
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
7
of
12
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
5
of
12
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
0
of
6
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
5
of
6
Significant Findings Finger Kinematics:
9. Thumb Kinematics
A computer kinematic assessment is performed for thumb flexion/extension.
The Examinee is asked to perform each maneuver 8-10 repetitions to full range and as quickly as possible.
The events are video taped in a precisely calibrated field for computer analysis.
Each event is analyzed for total dynamic range of motion and peak velocity quantity
and quality. Consistency of results is considered for
determining Examinee effort. After a thorough discussion of expectations, and
agreement of understanding by the Examinee, the Examinee is asked to perform
the movement events.
|
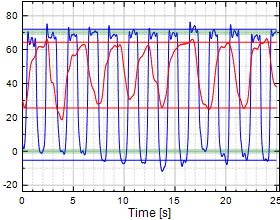
Chart 14:
Thumb MP Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 14:
Thumb MP Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
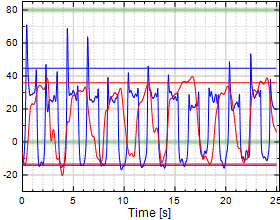
Chart 15:
Thumb IP Flexion/Extension
|
|
|
|
Table 15:
Thumb IP Flexion/Extension (F/E)
[
Help
]
|
|
|
|
|
Summary 9:
Thumb Kinematics
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
4
of
8
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
3
of
8
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
0
of
4
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
3
of
4
Significant Findings Thumb Kinematics:
|
Summary :
FCE - KinCon Report
|
|
|
- Number of tests where Examinee performed subnormal:
27
of
54
- Number of tests where Examinee performed asymmetrically (one side worse than the other):
20
of
54
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Left Side than on Right Side:
3
of
24
- Number of tests where Examinee performed worse on Right Side than on Left Side:
16
of
24
Significant Findings FCE - KinCon Report:
10. Conclusions